Cooking Up Cloud: Fargate or EC2—Which Kitchen Suits You?
The Amazon Elastic Container Service (ECS) from Amazon deploys and manages containerised applications in two distinct modes of operation: Fargate and self-managed EC2. Each offering has its strengths and is different from the other, making the choice between them a critical decision for businesses.
This blog discusses some of the more prominent differences between AWS ECS Fargate and EC2: architectures, advantages, challenges, and cost implications of running workloads in ECS Fargate versus ECS EC2. Whether you’re looking for operational simplicity or maximum control over infrastructure, this guide will help you navigate the differences between these two powerful container orchestration modes.
FARGATE: A Chef At The Restaurant
AWS Fargate is a serverless compute engine for containers that abstracts the complexities of managing the underlying infrastructure. With Fargate, you can focus solely on building and deploying your containerised applications without worrying about provisioning, configuring, or scaling virtual machines.
This fully managed service automatically handles scaling, load balancing, and networking, allowing you to allocate resources precisely based on your application’s needs. Whether running microservices, batch jobs, or other containerised workloads, Fargate provides a simplified, efficient, and secure environment that adapts to dynamic demands, just like a Chef at a restaurant who cooks everything for you. The only input they need is what you will eat.

EC2: A Home’s Kitchen
Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) is a flexible and scalable cloud computing service that provides virtual servers, known as instances, for various applications. With EC2, you have complete control over the operating system, instance types, and configurations, allowing you to customise your environment to meet specific needs.
Whether hosting web applications, running batch processes, or managing complex workflows, EC2 offers a robust and adaptable infrastructure tailored to your performance and cost requirements. By choosing from various instance types and sizes, you can optimise resource allocation and scale your infrastructure as needed, all while maintaining control over the underlying hardware and software, just like a typical Home Kitchen where you decide what you will cook with complete granular control over everything.

FARGATE vs EC2: What are the differences?
Understanding their fundamental differences is crucial when choosing between AWS Fargate and EC2 for your containerised applications. Each mode offers unique advantages and trade-offs across various deployment, management, and cost aspects. Here’s a brief comparison to help you identify which option best suits your needs.
| FARGATE | EC2 | |
|---|---|---|
| Infrastructure Management | Serverless; abstracts infrastructure management, allowing you to focus solely on your containers. | Requires manual management of virtual machines, including provisioning, configuration, and scaling. |
| Resource Allocation | Pay-per-task based on vCPU and memory; dynamically allocates resources based on task requirements. | Fixed costs based on instance type; you pay for the entire instance regardless of how much its capacity is used. |
| Scalability | Automatically scales based on task requirements; no need for manual intervention. | Requires manual scaling or configuration of auto-scaling groups to adjust capacity. |
| Operational Overhead | Low operational overhead; AWS handles server management, patching, and scaling. | Higher operational overhead; you manage server maintenance, patching, and scaling. |
| Customization | Limited customisation of underlying infrastructure; focuses on container management. | High customisation; you have full control over instance types, storage options, and network configurations. |
| Cost Efficiency | Ideal for unpredictable workloads with variable resource needs; pay only for the resources used. | More cost-effective for consistent, high-utilization workloads; offers various pricing plans like Savings Plans and Reserved Instances. |
| Performance Optimization | Resource limits are predefined; require monitoring and adjustment to optimise performance. | Allows for detailed benchmarking and tuning of resources to match specific performance needs. |
ECS w/ FARGATE
When using ECS with Fargate, you define your application’s requirements, such as CPU and memory, and Fargate handles the rest. This includes provisioning, scaling, and managing server infrastructure, allowing you to focus solely on developing and deploying your applications (read more).
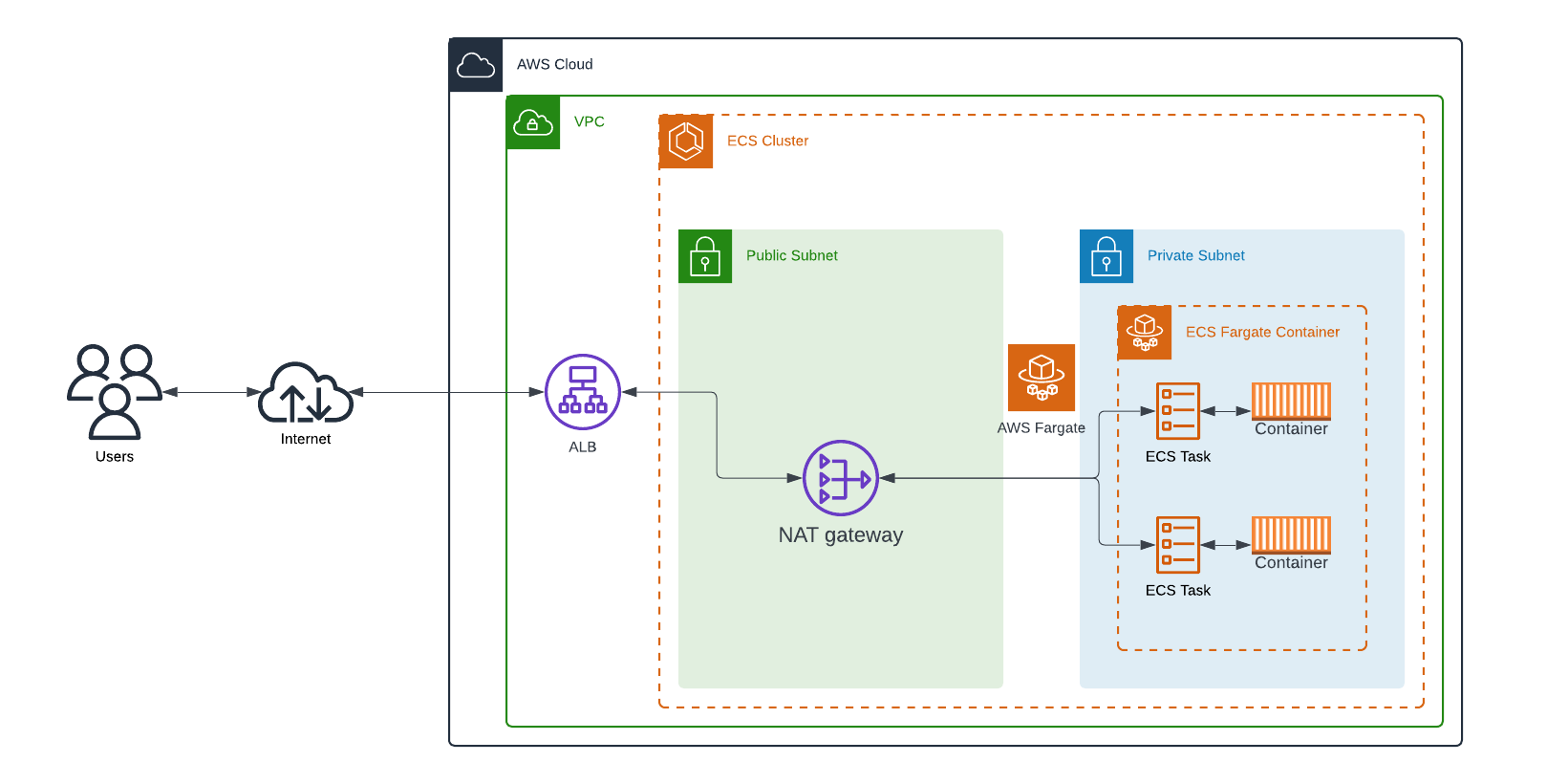
ECS w/ EC2
When using ECS with EC2, you have complete control over the underlying infrastructure that runs your containerised applications. This approach allows you to provision and manage EC2 instances, selecting specific instance types, sizes, and configurations that best meet your application’s needs. With ECS on EC2, you manage the cluster’s capacity, including scaling, patching, and maintaining the instances. This offers greater flexibility for performance tuning, custom networking setups, and the ability to use GPUs (read more).
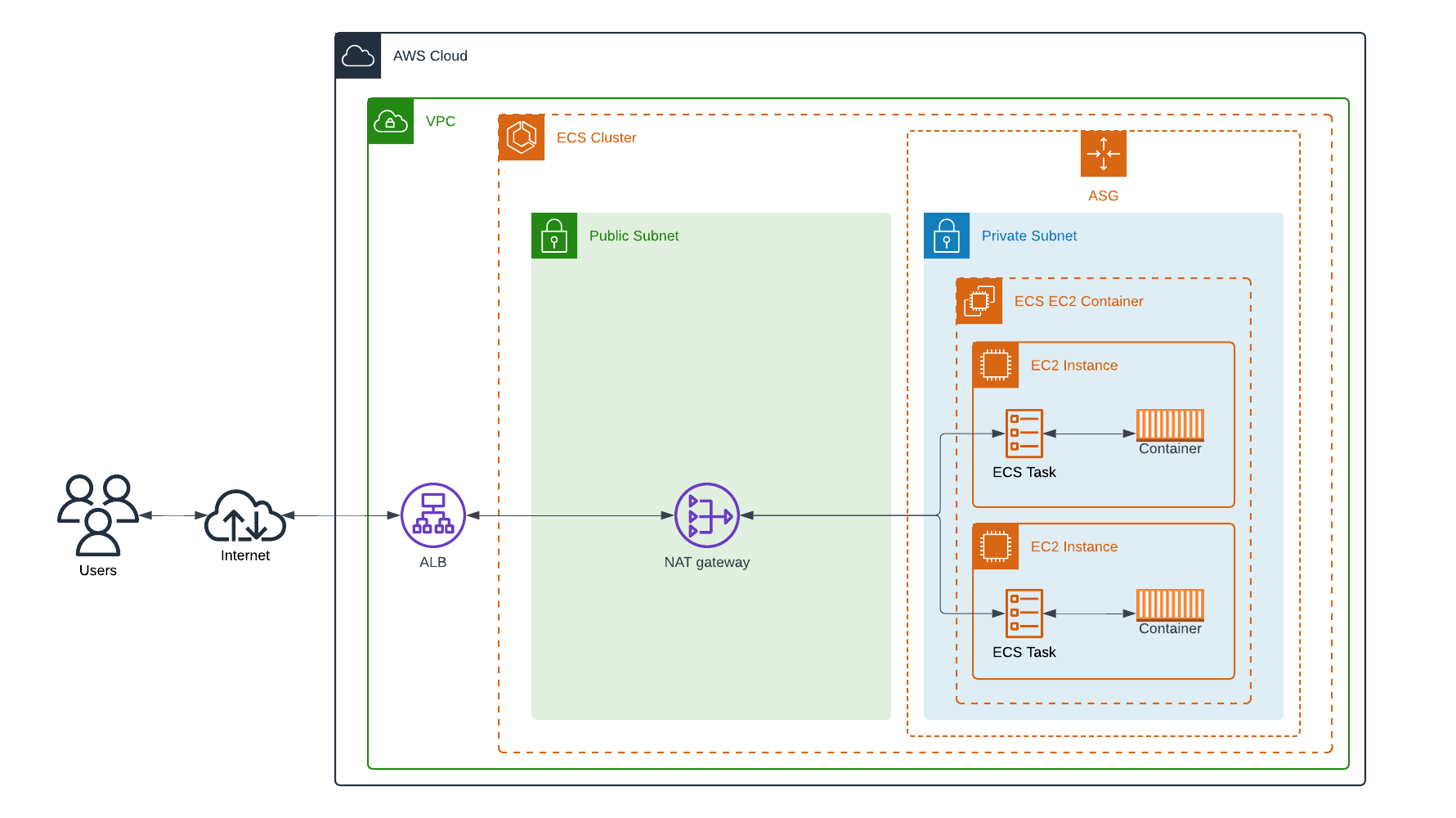
However, it also comes with increased operational overhead, as you need to ensure the infrastructure is managed correctly and optimised for your workload. This mode is ideal for scenarios requiring detailed control and customisation of the computing environment.
FARGATE vs EC2: Cost Analysis
When deciding between AWS Fargate and EC2, understanding the cost difference can make or break your decision. Let’s compare the costs for our specific setup. Please note that the following cost estimates for the services fall in the ap-south-1 region (i.e., Mumbai).
| Resource | Allocation |
|---|---|
| vCPU | 2 |
| Memory | 4 GB |
| Storage | 20 GB |
| Operating System | Linux |
| CPU Architecture | x86 |
Fargate Costs
With Fargate, you’re paying directly for the resources your tasks use. In our case, running a task continuously for a month raises a bill of about $75.73. This includes everything from vCPU and memory charges, with storage thrown in for free (thanks to the 20 GB free tier). The selling point of Fargate is that you don’t have to worry about managing the infrastructure, but that convenience comes with a higher price tag, especially if your workload is always on.
1 task × 2 vCPU × 730 hours × $0.04256 per hour = $62.14 for vCPU hours
1 task × 4.00 GB × 730 hours × $0.004655 per GB per hour = $13.59 for GB hours
20 GB - 20 GB (no additional charge) = $0.00 billable ephemeral storage per task
Total Fargate cost (monthly): $75.73
EC2 Costs
Running the same workload on EC2 gives you a few pricing paths:
-
On-Demand Pricing
If you go the on-demand route, the monthly cost is about $18.17. This covers both the instance and storage costs. It’s the most flexible option, but you’re paying more per hour.
On-Demand Hourly cost: $0.0224
1 instance × $0.0224 × 730 hours in a month = $16.35
20 GB × 1 instance months × $0.0912 = $1.82 (EBS Storage Cost)
Total On-Demand cost (monthly): $18.17
-
Compute Savings Plan
With a 1-year commitment and no upfront cost, this drops the monthly price to $13.65, 25% cheaper than On-Demand instances. It’s a solid choice if your workload is predictable, offering decent savings over on-demand pricing.
Hourly cost: $0.0162
1 instance × $0.0162 × 730 hours in a month = $11.83
20 GB × 1 instance months × $0.0912 = $1.82 (EBS Storage Cost)
Total Compute Savings Plan cost (monthly): $13.65
-
EC2 Instance Savings Plan
This is the cheapest option, costing around $12.19 per month, about 33% cheaper than On-Demand. You’ll need to commit to a specific instance type, but if that fits your needs, it’s the way to go for maximum savings.
Hourly cost: $0.0142
1 instance × $0.0142 × 730 hours in a month = $10.37
20 GB × 1 instance months × $0.0912 = $1.82 (EBS Storage Cost)
Total EC2 Instance Savings Plan cost (monthly): $12.19
The Point Is
Fargate’s higher price includes reduced operational hassle, automatic scaling, and simplicity—big perks if your workload is dynamic or unpredictable. Conversely, if your workload is steady and you like having more control, EC2 could be your better bet. So, choosing EC2 could save you up to 84% compared to Fargate, depending on your pricing plan. That’s some serious savings to consider when making your choice!
Conclusion
In conclusion, choosing between AWS Fargate and EC2 involves balancing your specific needs with the strengths and trade-offs each mode offers. Fargate simplifies container management with a fully managed, serverless environment, making it ideal for dynamic workloads and teams focused on reducing operational overhead. On the other hand, EC2 offers more control and cost efficiency, especially with Savings Plans, making it a better fit for steady, predictable workloads where performance tuning and customization are key. Ultimately, the best choice depends on your workload’s demands and your team’s priorities—whether it’s simplicity and flexibility or control and cost savings.
Until next time, Happy Coding.




